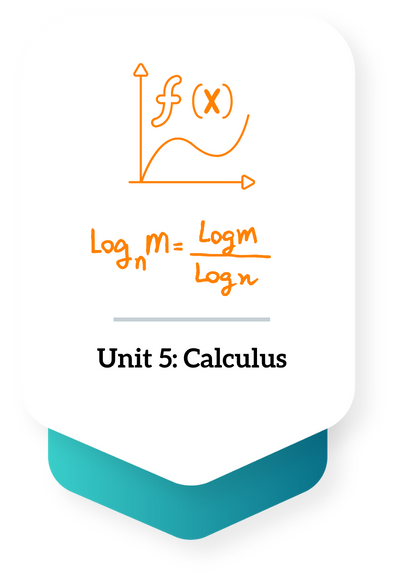
Table of Contents1 Unit 1: Number and Algebra 2 Unit 2: Functions3 Unit 3: Geometry and trigonometry4 Unit 4: Probability and Statistics5 Unit 5: Calculus Unit 1: Number and Algebra Chapter Number IB Points to Understand 1.1 Conducting mathematical operations with exponential numbers and expressing them in terms of a x (bk) where a ranges from 0 < a < 10. 1.2 Sequence- A sequence is a list of numbers that is written in a defined order, ascending or descending, following a specific rule. Series- A series is the sum of all the terms in a sequence. A finite sequence has a fixed number of terms. An infinite sequence has an infinite number of terms. A term in a sequence is named using the notation 𝑎𝑛, where 𝑛 is the position of the term in the sequence. A term in a sequence is named using the notation 𝑎𝑛, where 𝑛 is the position of the term in the sequence. A sequence formed when each term after the first is found by adding a fixed non-zero number is called an arithmetic sequence. Adding up the terms of an arithmetic sequence gives us arithmetic series. 1.3 A sequence in which every term is obtained by multiplying or dividing a non-zero number with the preceding number is known as a geometric sequence. When 𝑟 > 1, the sequence is diverging. And when 𝑟 < 1, the sequence is converging. A geometric series with 𝑟 < 1 and with infinite number of terms is called an infinite geometric series. 1.4 Applications of Geometric sequences and series: Compound interest Population growth Annual Depreciation 1.5 Exponential operations and laws Logarithms and numerical evaluation of logarithms 1.6 Simple proofing techniques and deductive proof (LHS = RHS): Ex: Show that 1.7 Rational Exponents and solving its equations Laws of logarithms: (Change of Bases) 1.8 Infinite convergent geometric sequences and its summation 1.9 A binomial is a polynomial with two terms. Pascal’s triangle is a triangular array constructed by summing adjacent 1.10 (HL) Permutation relates to the act of arranging all the members of a set into some sequence or order, or if the set is already ordered, rearranging its elements, a process called permuting The combination is a way of selecting items from a collection, such that (unlike permutations) the order of selection does not matter. Binomials with fractional and negative indices 1.11 (HL) Partial fractions: Maximum of two distinct linear terms in the denominator, with degree of numerator less than the degree of the denominator. 1.12 (HL) Complex numbers: the number i, where i2 = − 1. Cartesian form z = a + bi; the terms real part, imaginary part, conjugate, modulus and argument. 1.13 (HL) Modulus–argument (polar) form: z = r(cosθ + isinθ) = rcisθ. Euler form: z = reiθ 1.14 (HL) Complex conjugate roots of quadratic and polynomial equations with real coefficients. De Moivre’s theorem and its extension to rational exponents. Powers and roots of complex numbers. 1.15 (HL) Proof by mathematical induction Proof by contradiction Proof by counterexample to denote a statement sometimes isn’t always true 1.16 (HL) Solutions of systems of linear equations (a maximum of three equations in three unknowns), including cases where there is a unique solution, an infinite number of solutions or no solution. Unit 2: Functions Chapter number IB Points to Understand 2.1 Various equations denoting a straight line: General Form (ax + by + d = 0) Gradient Intercept Form (y = mx + c) Point Gradient Form( y – y1 ) = m( x – x1 ) Parallel lines (m1 = m2) Perpendicular lines () 2.2 Functions, domains, range and graph Notation of a function – f(x), v(t) etc. The inverse of a function will only exist if the function is one-to-one. The inverse of a function 𝑓 is denoted 𝑓−1 and is a reflection about the line y = x 2.3 Formation of the equation of a graph Construction of a graph utilising information given such as the equation 2.4 Determination of key features of a graph – maximum and minimum values, root values, intercepts, horizontal and vertical asymptotes, vertices of a given graph Intersection of two curves 2.5 Composite functions Identity functions and deriving inverse function 2.6 Quadratic functions – (f(x) = ax2 + bx +c) Y-intercept, axis of symmetry and its graph(parabola) X-intercepts – f(x) = a(x-p)(x-q) where (p,0) and (q,0) are x-intercepts Vertex of a quadratic graph – f(x) = a(x – h)2 + k, where (h, k) is the coordinates of the vertex 2.7 Solution of quadratic equations and inequalities and the quadratic formula. The discriminant Δ = b2 − 4ac and the nature of the roots, that is, two distinct real roots, two equal real roots, no real roots. 2.8 Reciprocal function along with their graphical representation and its self-inverse nature Rational functions – along with their graphical representation Vertical and Horizontal Asymptote equations 2.9 Exponential functions and their graphs: f(x) = ax, a > 0, f(x) = ex Logarithmic functions and their graphs: f(x)=logax, x > 0, f(x)=lnx, x > 0. 2.10 Solving equations both graphically and analytically Use of technology to solve a variety of equations, including those where there is no appropriate analytic approach. Applications of graphing skills and solving equations that relate to real-life situations. 2.11 Transformations of graphs: Translations: y = f(x) + b; y = f(x − a) Reflections (in both axes): y = − f(x); y = f( − x) Vertical stretch with scale factor p: y = p f (x). Horizontal stretch with scale factor 1/q : y = f (qx) Composite transformations 2.12 (HL) Polynomial functions, their graphs and equations; zeros, roots and factors. The factor and remainder theorems. Sum and product of the roots of polynomial equations. 2.13 (HL) Rational functions (Graphs, reciprocal functions) 2.14 (HL) Odd and even functions Finding the inverse function, f-1 (x), including domain restriction Self-inverse functions 2.15 (HL) Solutions of g(x) ≥ f (x), both graphically and analytically. 2.16 (HL) The graphs of the functions,
IB Maths Application & Interpretation HL Tutors
The best solutions to all your math problems
Plus we won’t take away your PE classes
check out our results
Request Free Trial Class
We stand out for a reason
Numbers Tell Stories

Monthly progress reports
It will tell you where you stand and how much you’ve improved. It will not seem like a report card - some anxiety saved there, don’t worry.

Seamless Communication on Whatsapp groups
We add you into a group and you stay in the loop. It’s as easy as that.

IB Study materials, Question Banks, etc
We have an exhaustive library of resources for all our subjects. If you go through them all, you’ll be the superhero of knowledge.
Individual doubt clearing sessions
Personalized attention in one-on-one sessions are important. These sessions are to clarify every doubts that the student has.

Individual IA and EE sessions
We extend our hand to aiding with IA’s and EE’s. Long essays, check. Going through multiple drafts, check.

IB style test series
We conduct a series of tests in IB exam style conditions to help prep for the final exam. If it's nerve-wracking, then we know we’ve done a good job.

Toppers talk
There’s nothing more that impacts you than experiences. You will have the opportunity to hear some of our toppers' stories and how their dreams came true.

Sessions from IB examiners
We will have sessions with IB examiners for them to tell you what it is they look for in everything.
Best Online IB Maths Application & Interpretation HL Tutors
Secure your child’s future at Tychr.
The probability of you getting a 7 is rather high given the statistics of the average score of our IB Math students. “IB Math is no joke. It is not fun and it is not doable.” We’ll help you change that mindset to: “We’ll sit in the front row to answer all the questions. We’ll sound super smart.” Tychr’s IB math tutors are not professors. They’ve been through the “I used to hate IB Math” phase yet they were toppers in school. Hence, our IB math tutors are professional and creative with their teaching methods.
Semester wise approach
Calculus of Curiosity
-
Semester 1
-
Semester 2
-
Semester 3
-
Semester 4









Our Proven T.E.S.T. Methodology
Like all our online tuition, IB Maths Application & Interpretation HL follows our proven T.E.S.T. Methodology. For the IB Maths Application & Interpretation HL, this Means:
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
Lessons are prepared by credible IB Maths A&I tutors, and conduct doubt sessions, wherever needed.Intimidating theoretical topics like Calculus and its Applications and Functions are given more attention to make it comprehensive and engaging at the same time.
EXPLANATORY VIDEOS
Pre-recorded videos including topic coverage, tips and tricks, are provided so students independently and collaboratively extend their understanding of mathematics to strengthen student’s scoring ability !
STRENGTHENING CONCEPTS
The student then begins practicing topic-wise assignments to reinforce their learnings focusing on moral, social and ethical questions arising from the work of mathematicians. TYCHR also provides monthly progress reports to keep track of student’s performance.
TIME BOUND TEST SERIES
Finally, the student moves on to solving IB Maths A&I question papers in exam-style conditions for Paper 1 weighing 40% and 30% for HL , Paper 2 weighing 40% for SL and 30% for HL and and for Paper 3(HL) weighing 20% of the final grade. They then receive checked answer sheets and a comprehensive answer key to each.
How It Works?
Follow the well-grounded 6 step process to uncontested success


Request Free Trial Class
- It wasn’t too difficult to do the math to pick our tutors. Let us know how we’ve done.
- Mathematics. You need it for engineering, you need it for science, you need it for everything. We’ll help you score well in your papers and your IA/EE so you’re one step closer.
- 1 + 1 = 2 but do you know what Tychr + you equals? It’s a 7. It’s cringe, but if it works then don’t be hesitant. You’re making the right choice.
Summarized Syllabus
Mathematics the Elegant Logic
| Curriculum | Assessment |
Core Chapter 1: Number and Algebra Chapter 2: Functions Chapter 3: Geometry and trigonometry Chapter 4: Statistics and probability Chapter 5: Calculus | External Assessments: Paper 1: Section A: compulsory short-response questions based on the syllabus. Section B: compulsory extended-response questions based on the syllabus Paper 2: Section A: compulsory short-response questions based on the syllabus. Section B: compulsory extended-response questions based on the syllabus (HL) Paper 3: Two compulsory extended-response problem-solving questions. |
Elite Online IB Maths Application & Interpretation HL Tutors
Algebra: X-tra Fun @ Tychr

Individual attention
We offer students personalized teaching so they understand the depths of the Mathematics curriculum

Free Demo sessions
You can get a glimpse of what our sessions would be like before you decide to proceed with us.

Experienced Educators
Our tutors are aware of the changes of the curriculum to provide a complete understanding of what IB will expect in terms of answers and IA’s

Success Stories
Our tutors are here to guide you to the 7 you may need in Mathematics to get into the top tier colleges.

Credible
The extensive experience of our IB tutors are reflected in the quality of their teaching.

College Application guidance -
Our tutors are equipped to help you with your IA’s/EE depending on your career choice thus benefiting you during college applications
Don't forget to check our Forum
Don't forget to check our Forum
Our Expert Tutors!
- 12+ Years
Cat 1 – ESS and Cat 2 – Biology. Chief of the IB program. Mentored 320+ students across various curricula.
- 24+ Years
IBDP Physics HL / SL. IGCSE Physics. A-level Physics (AQA, CIE, Edexcel, OCR, and WJEC). IGCSE Physics (AQA,CIE, OCR & Edexcel)
- 9+ Years
IBDP Cat 1 – Business Management, IBDP Cat 1 – TOK. Taught over 130+ students across 4+ countries.
- 9+ Years
IBDP Cat 1 & 2 November 2019. Specializes in Global Politics. Many students scored 7s; mentors 200+ students in assessments.
- 16+ Years
Specializing in Mathematics: Analysis and Approaches (HL & SL), Mathematics: Applications and Interpretation (HL & SL), and MYP (Mathematics).
- 18 + Years
IBDP Cat 1 – Chemistry, IBDP Cat 3 – IA Chemistry, IBDP Cat 1 – TOK. Helped 2 out of 3 students achieve a 7 in IB Chemistry.
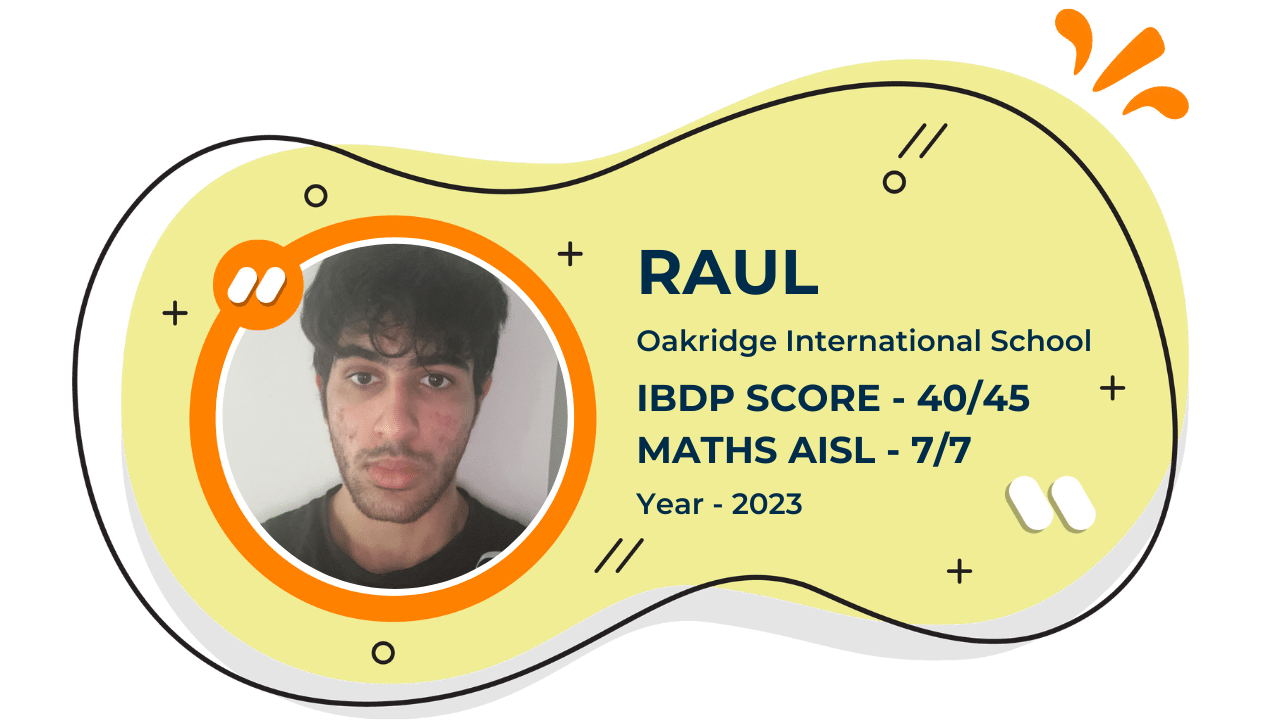
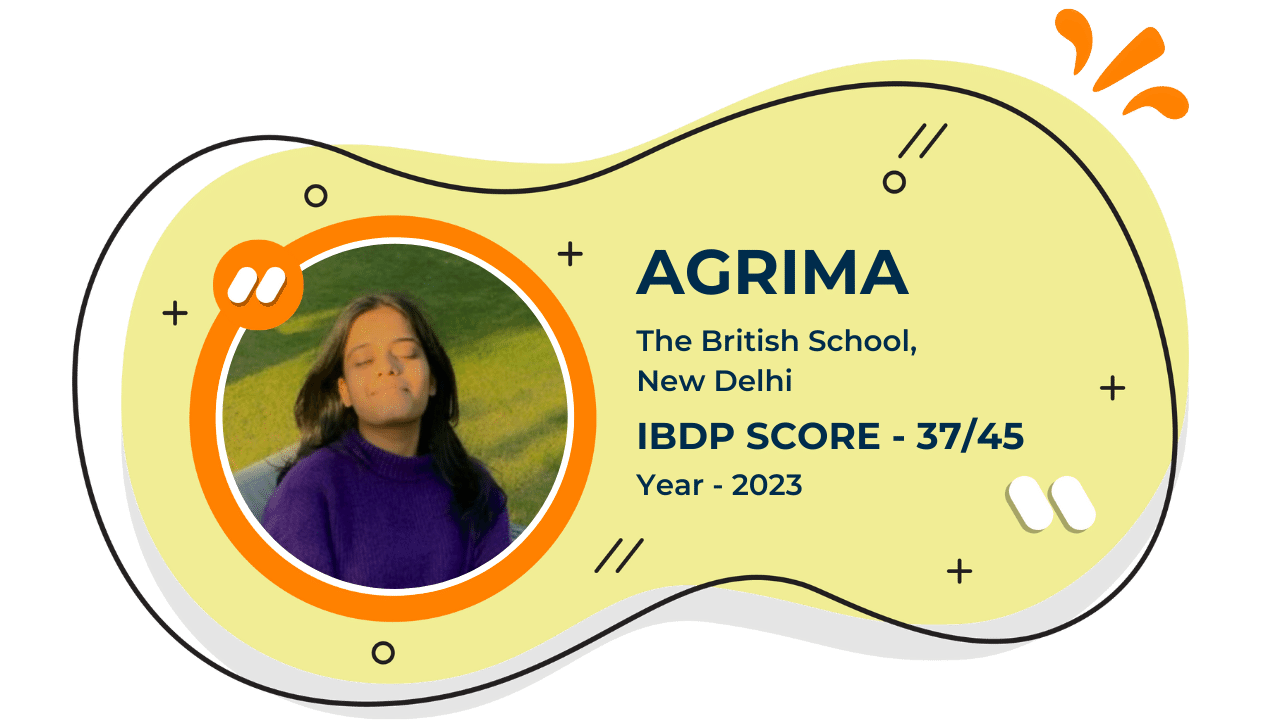
Our Student'S Results
Score 40+ in IB Exam like they did
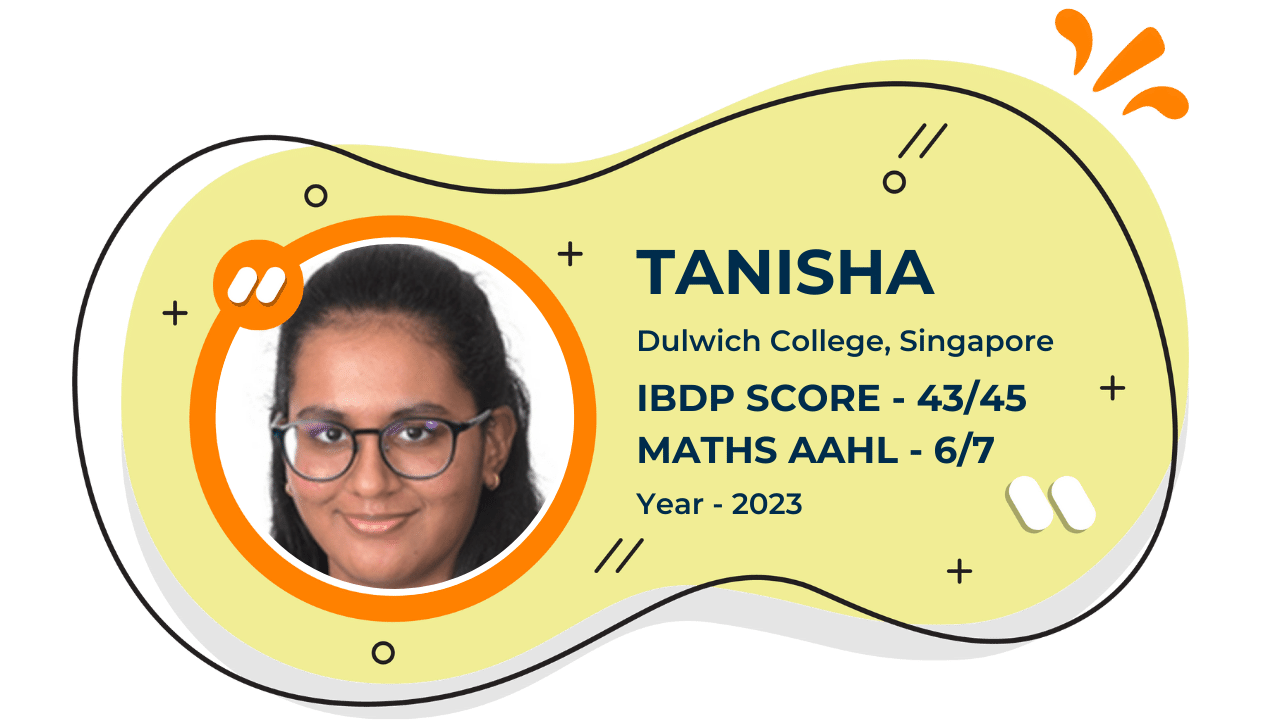
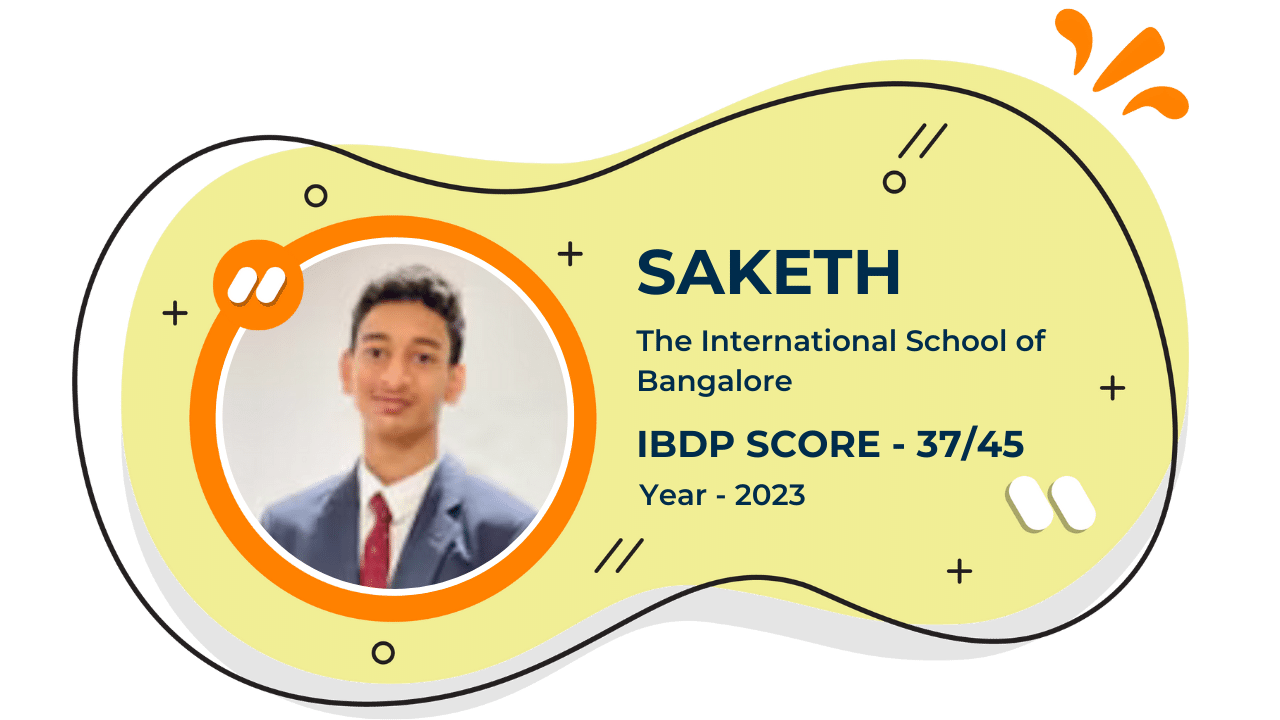
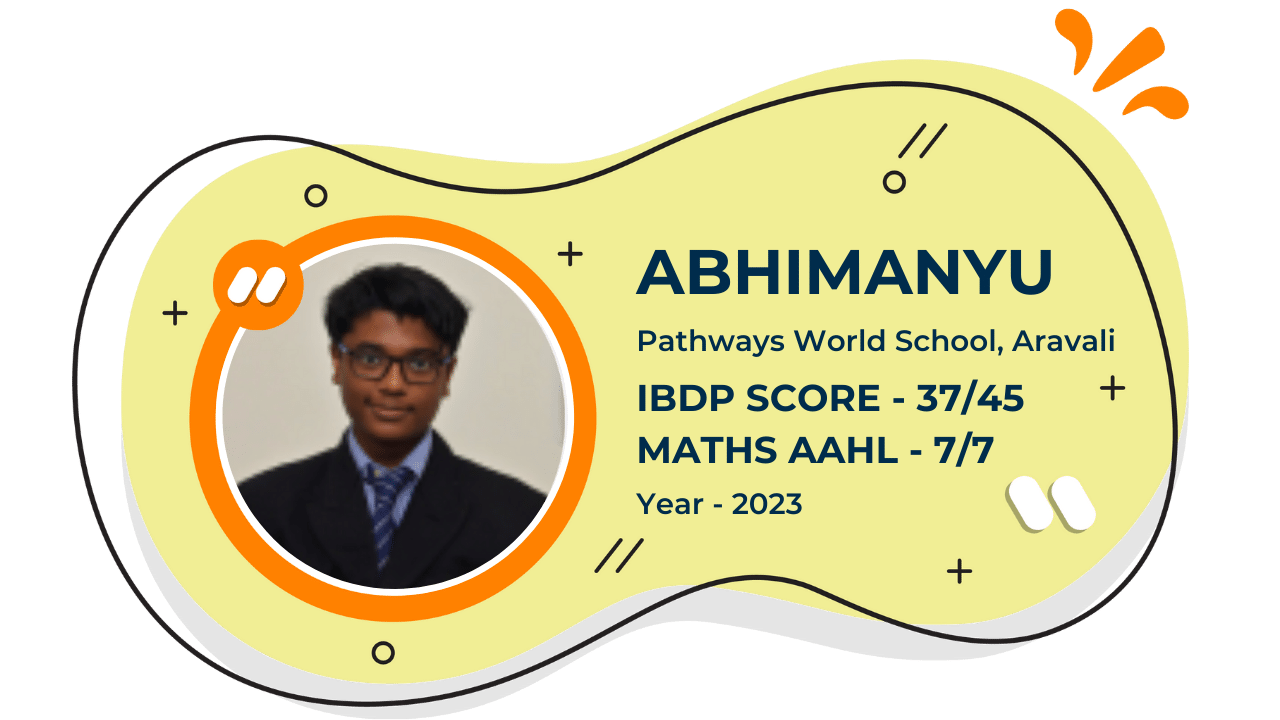
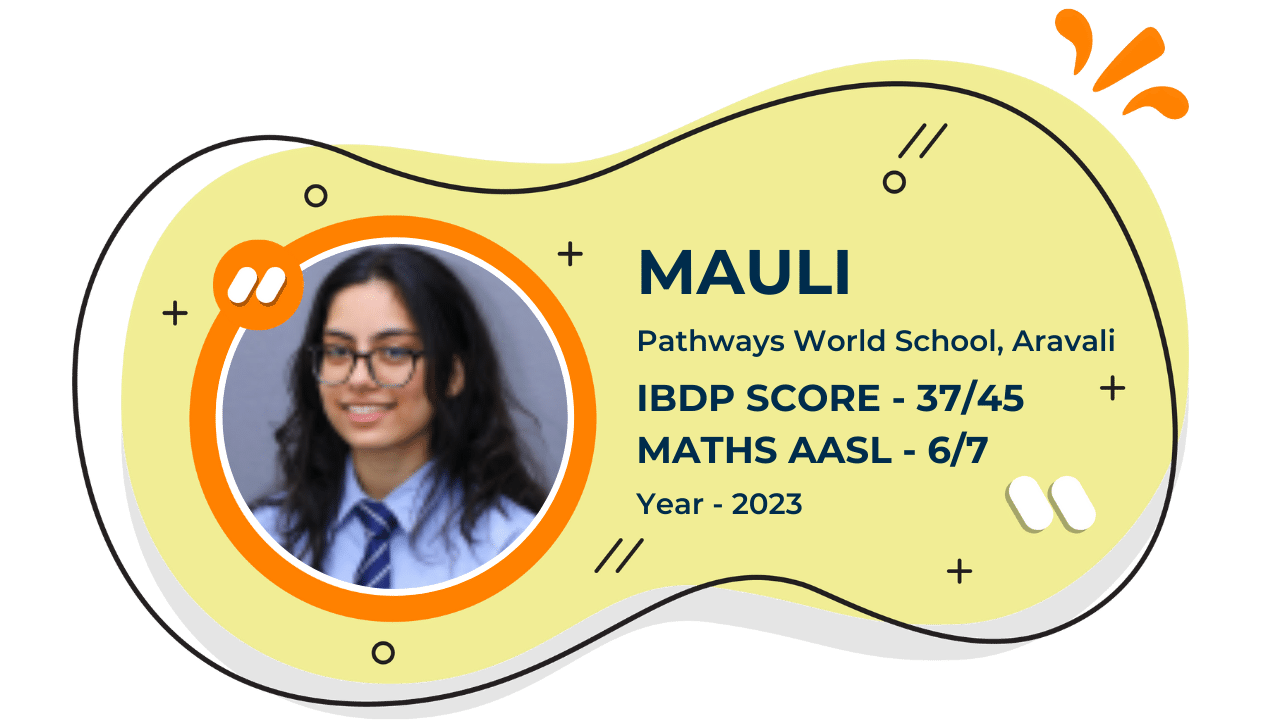

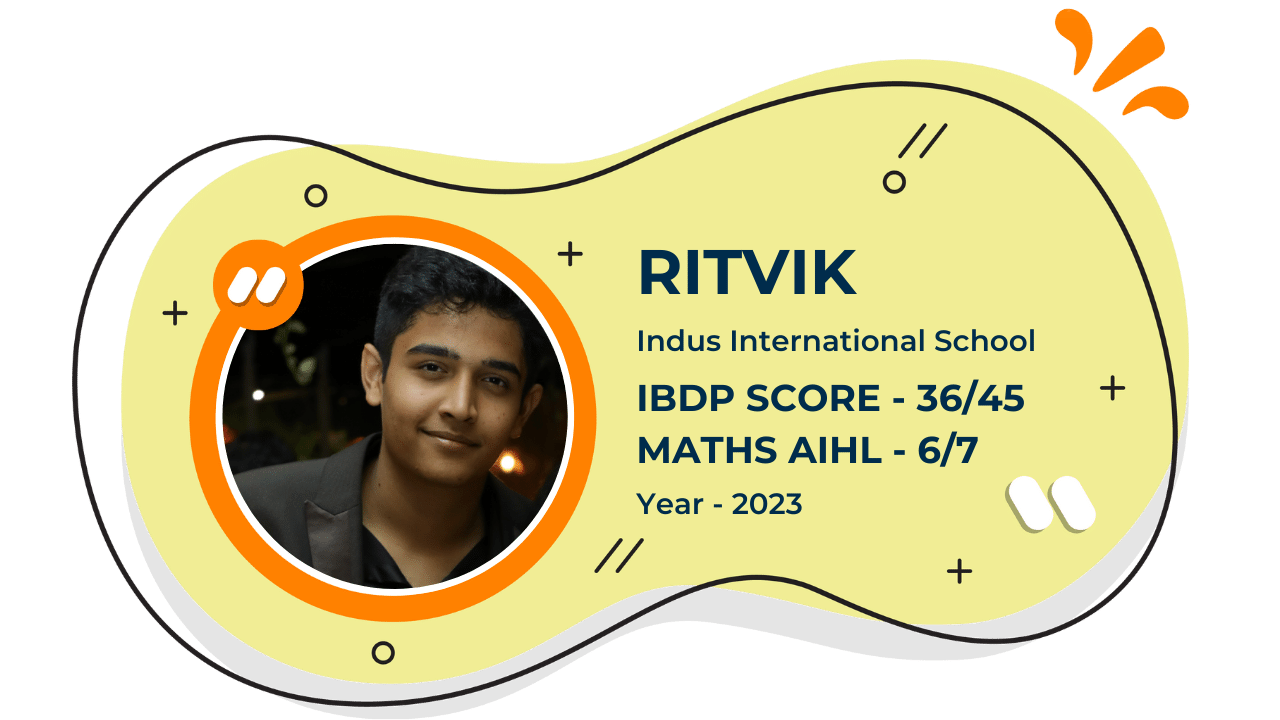
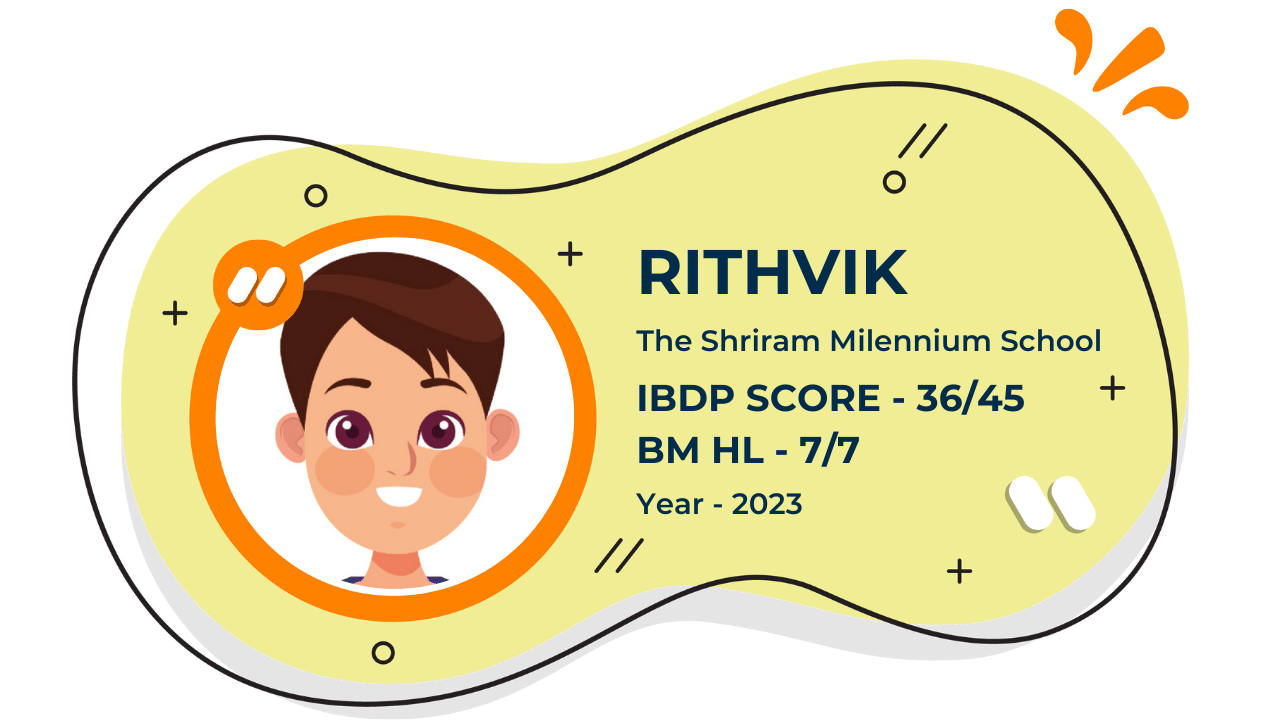
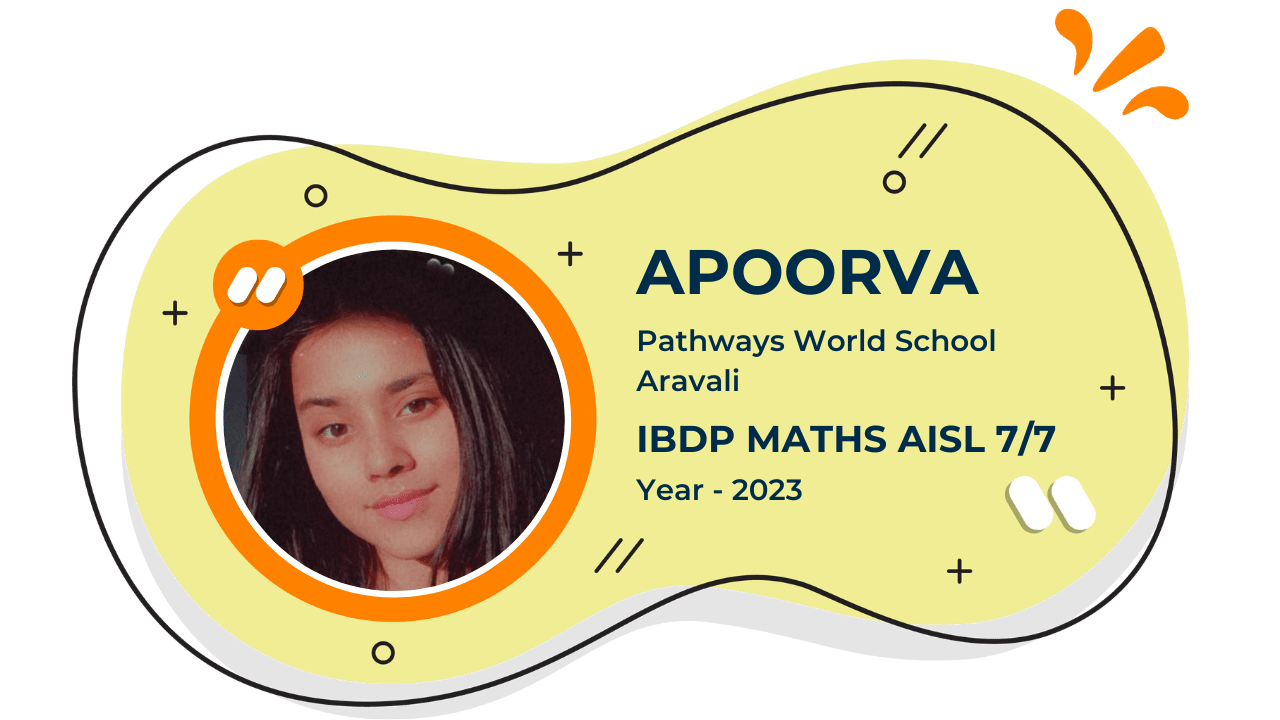
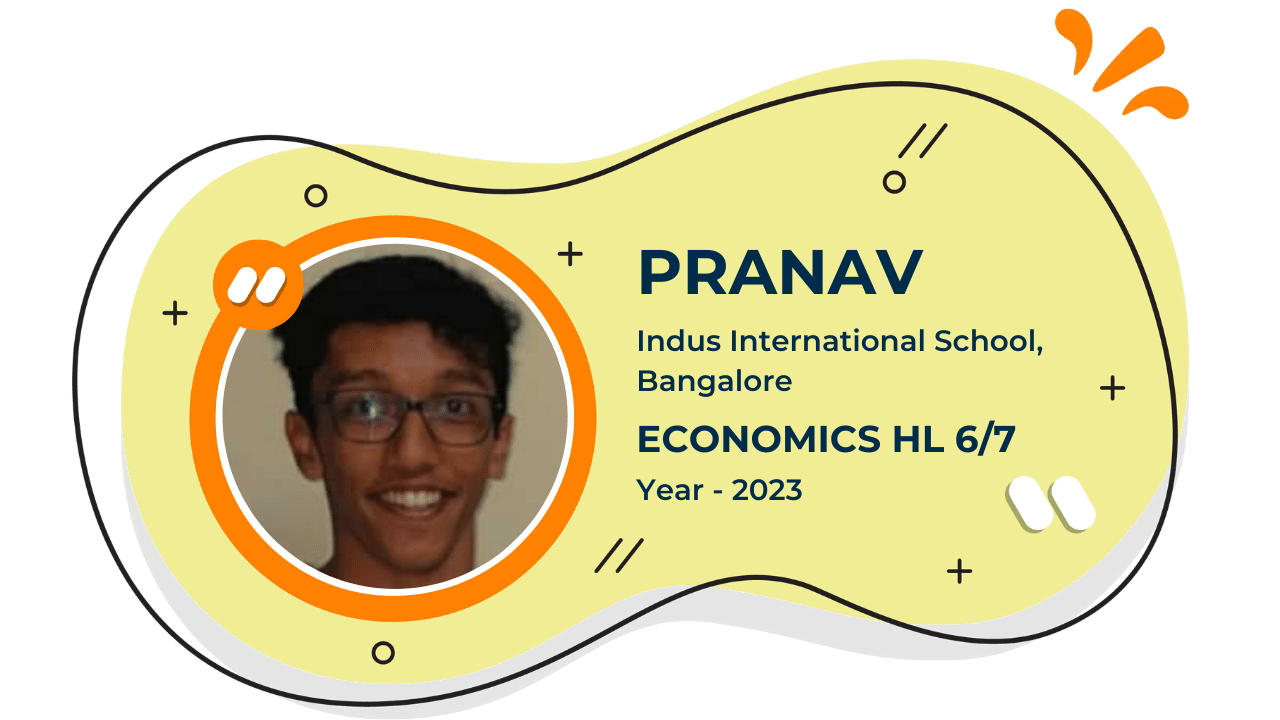
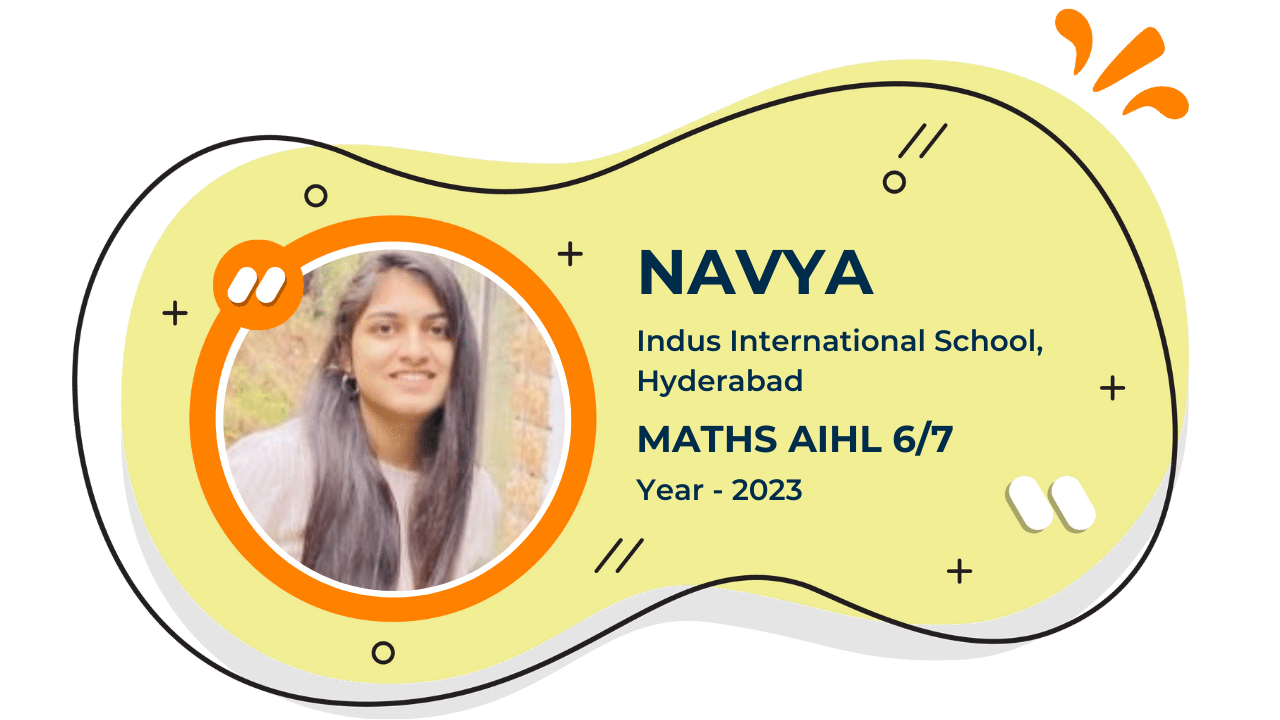
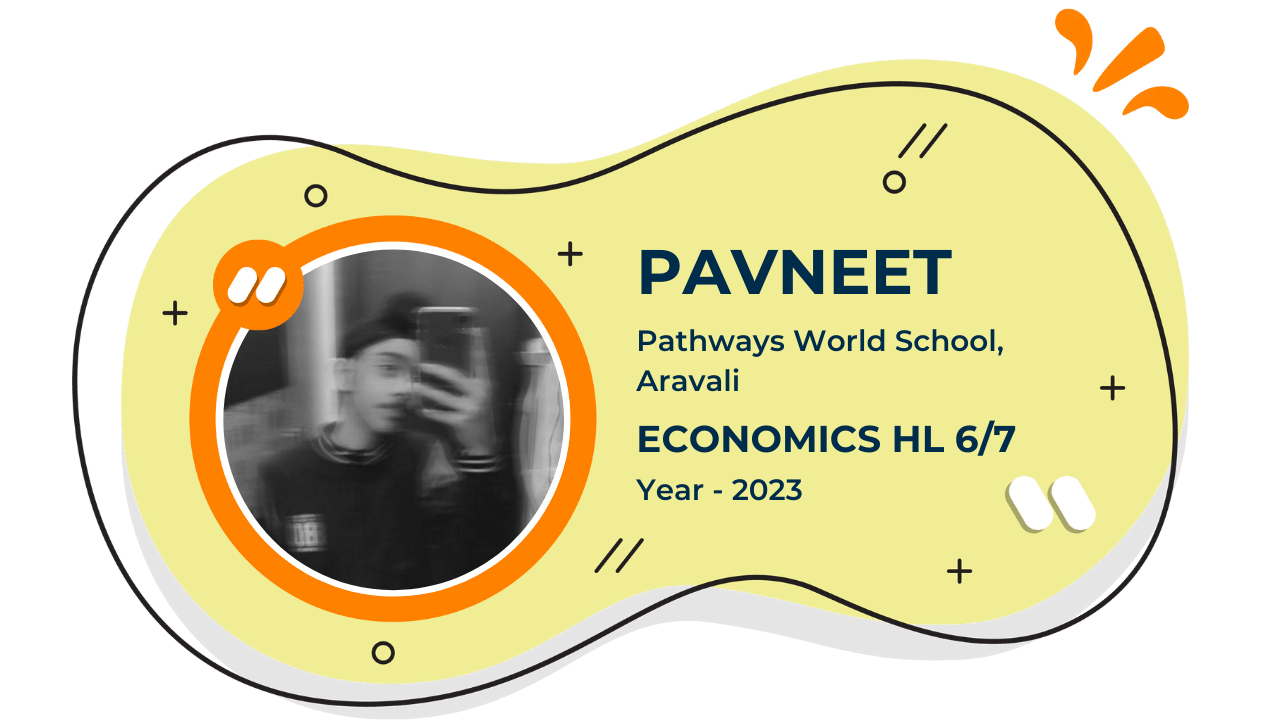
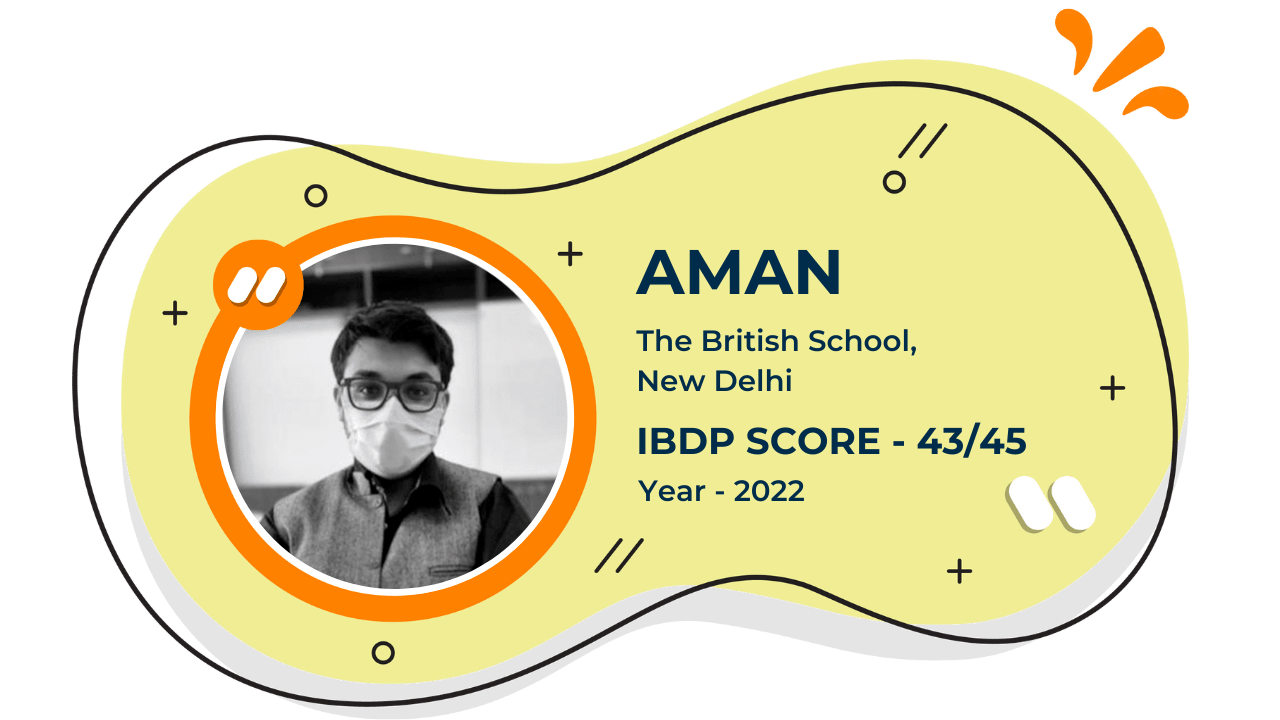
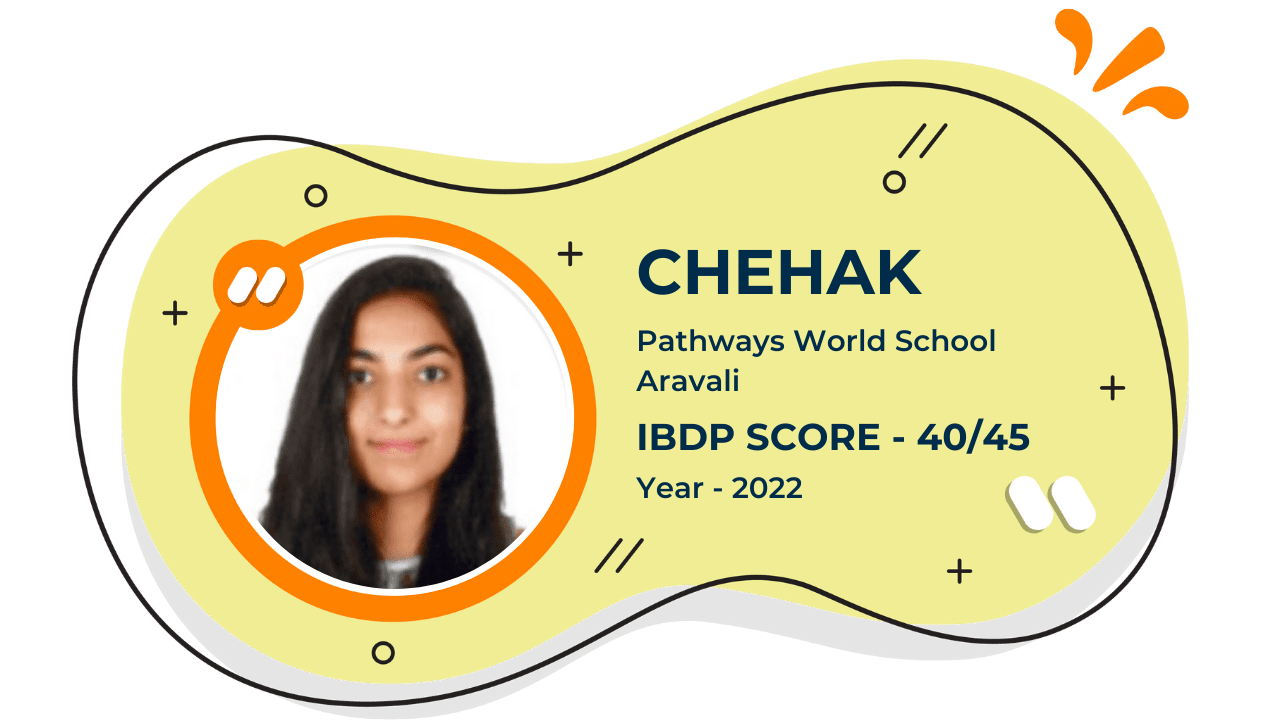
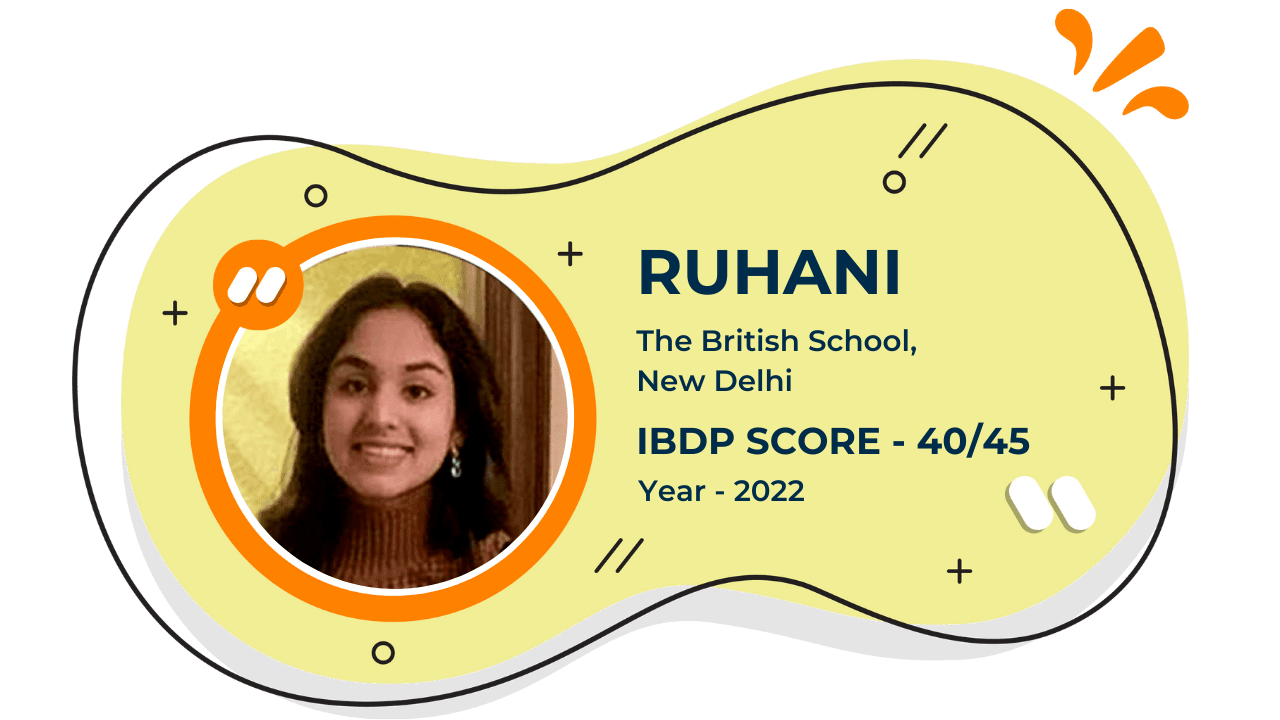


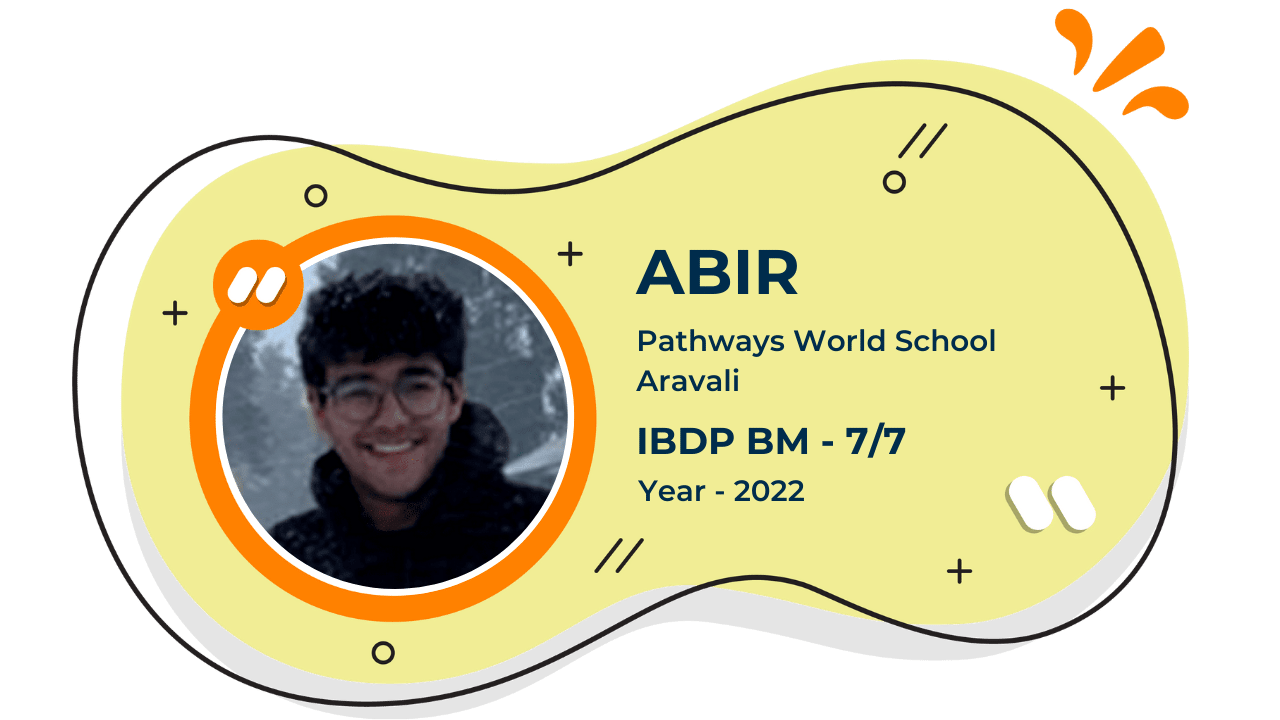
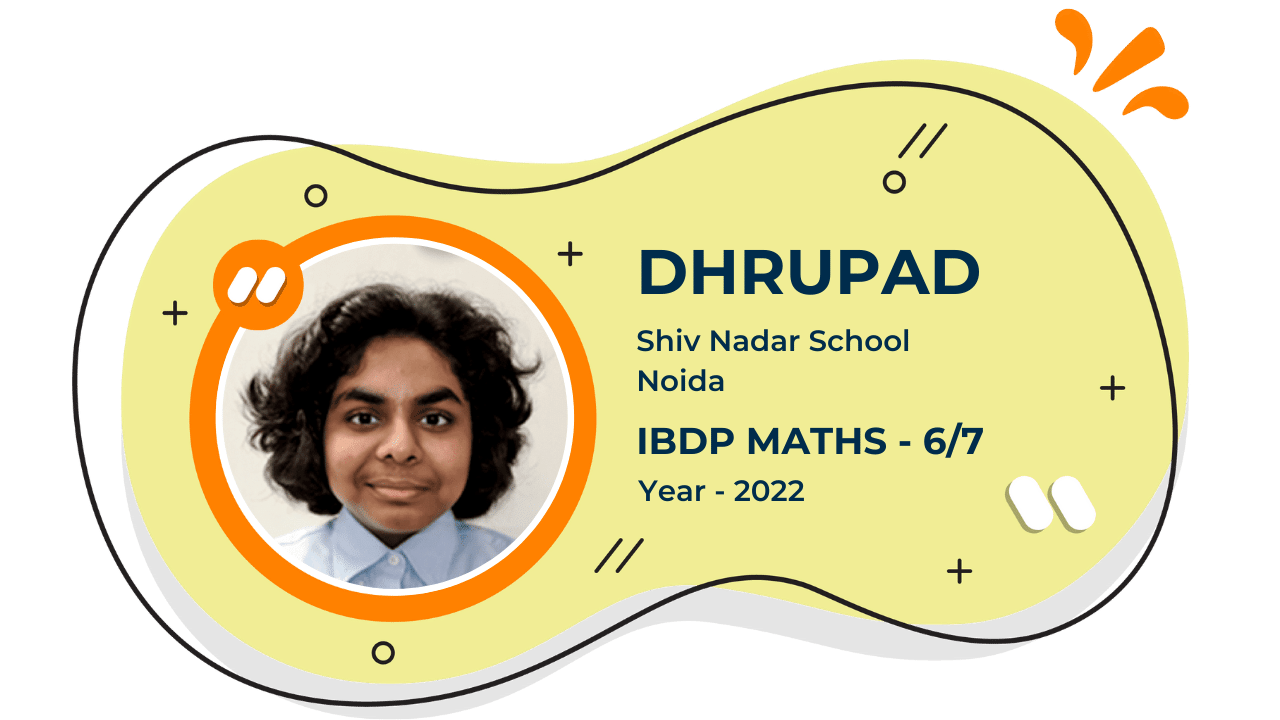
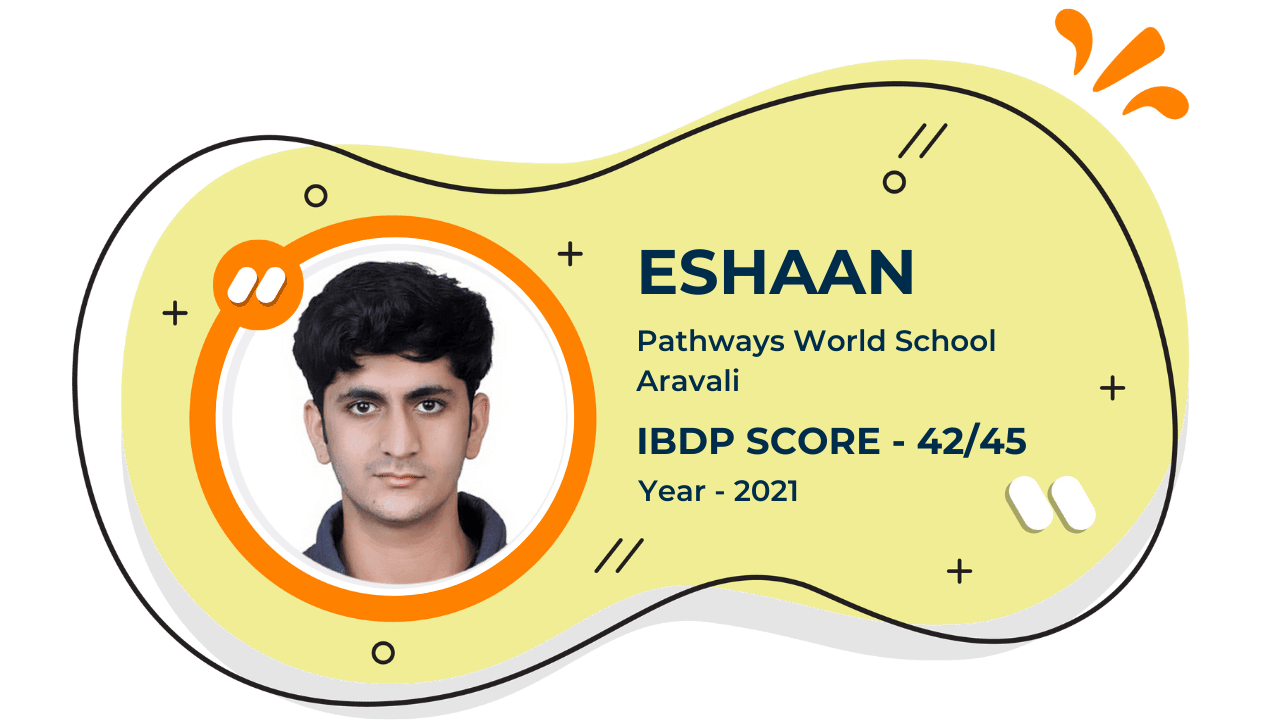
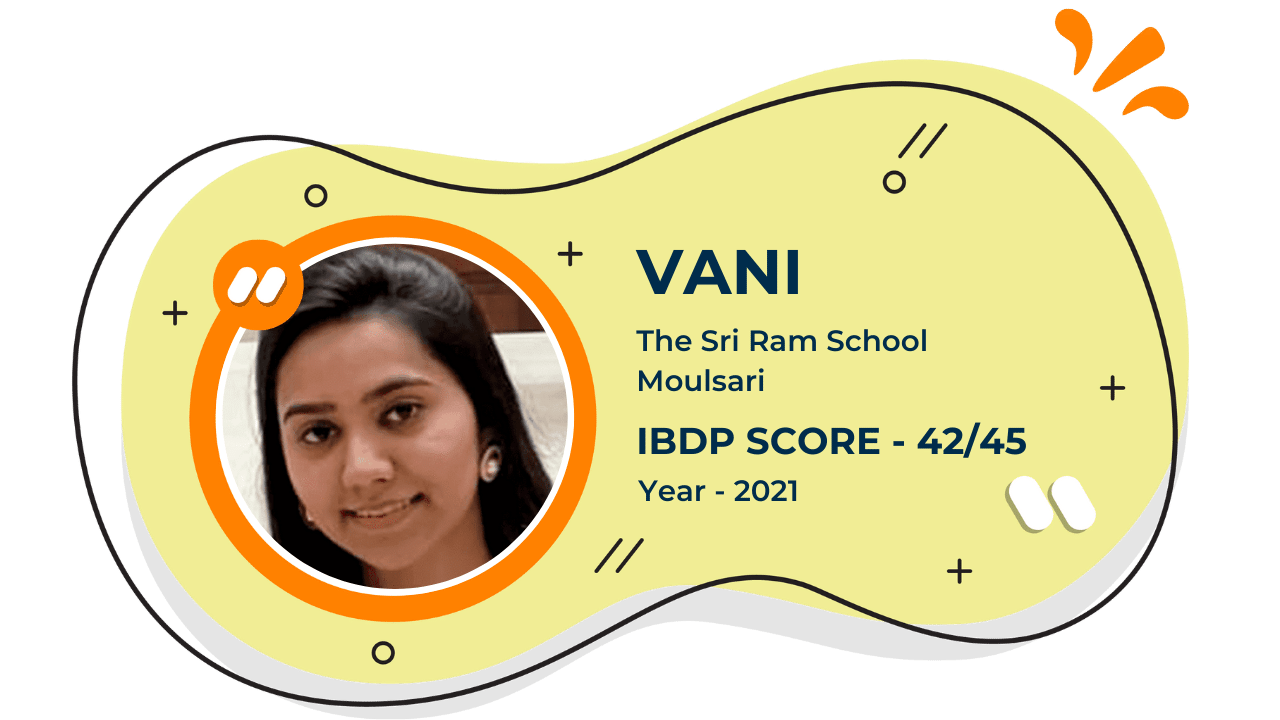


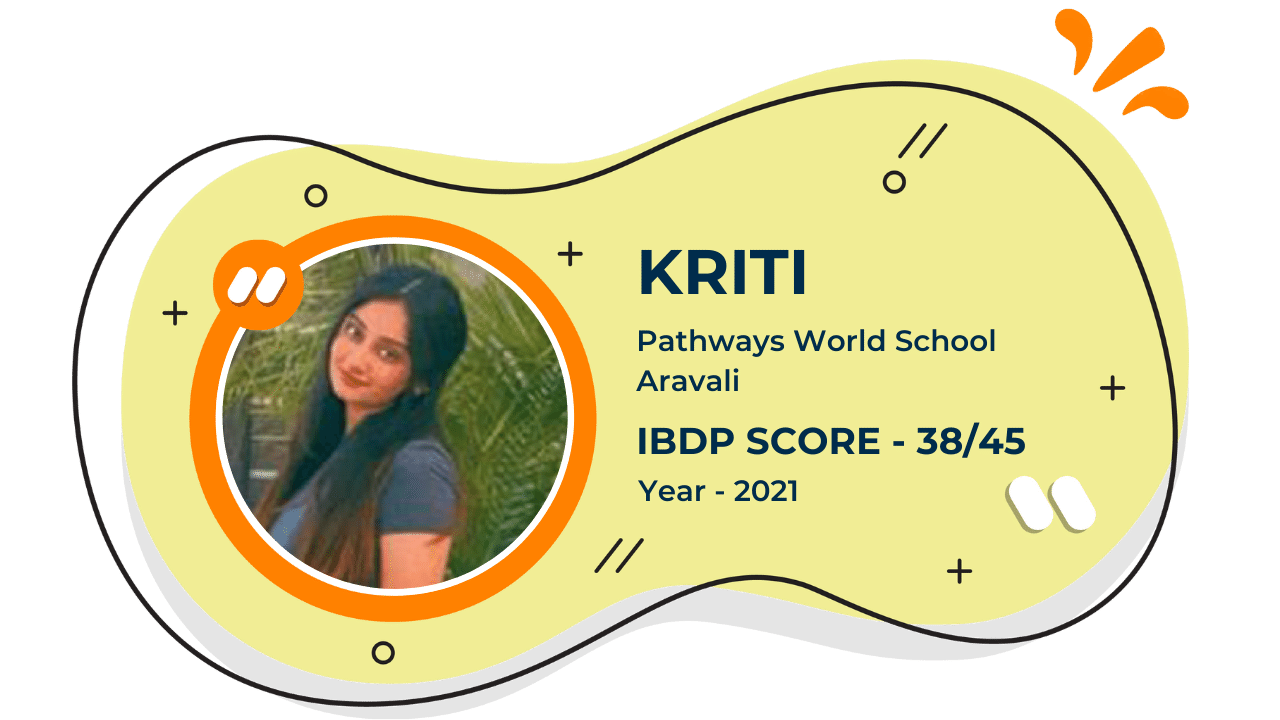
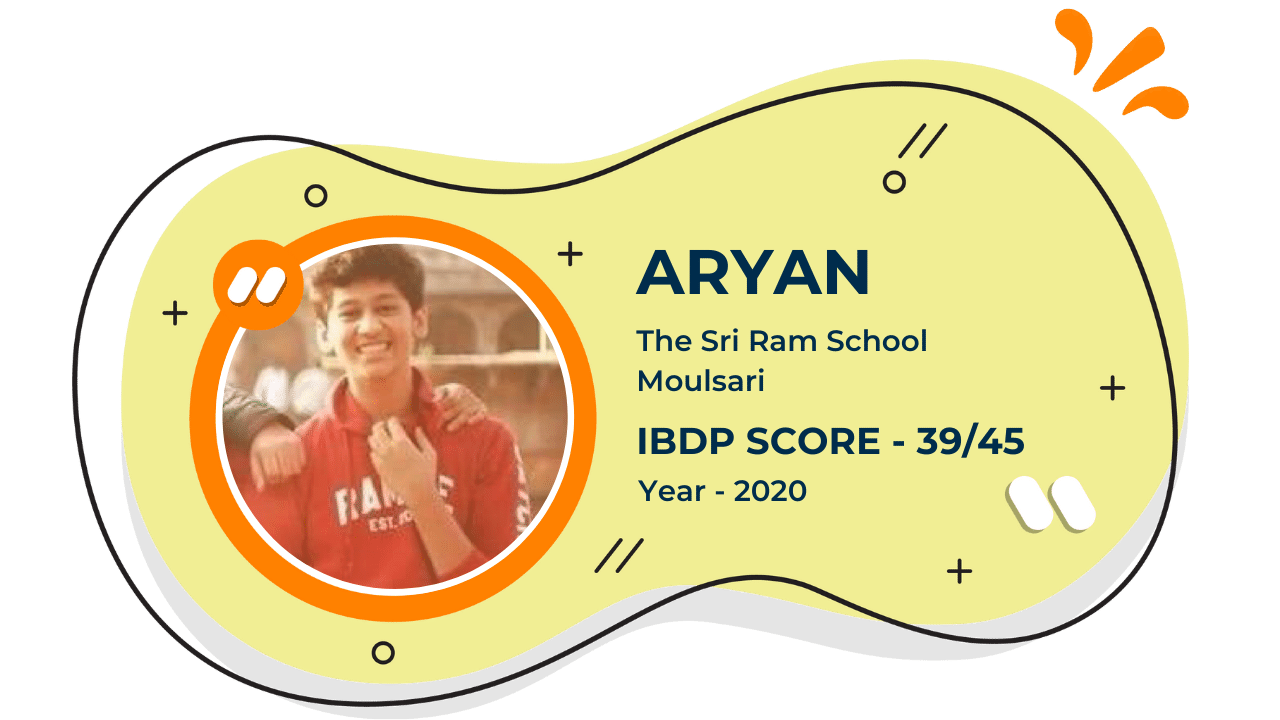
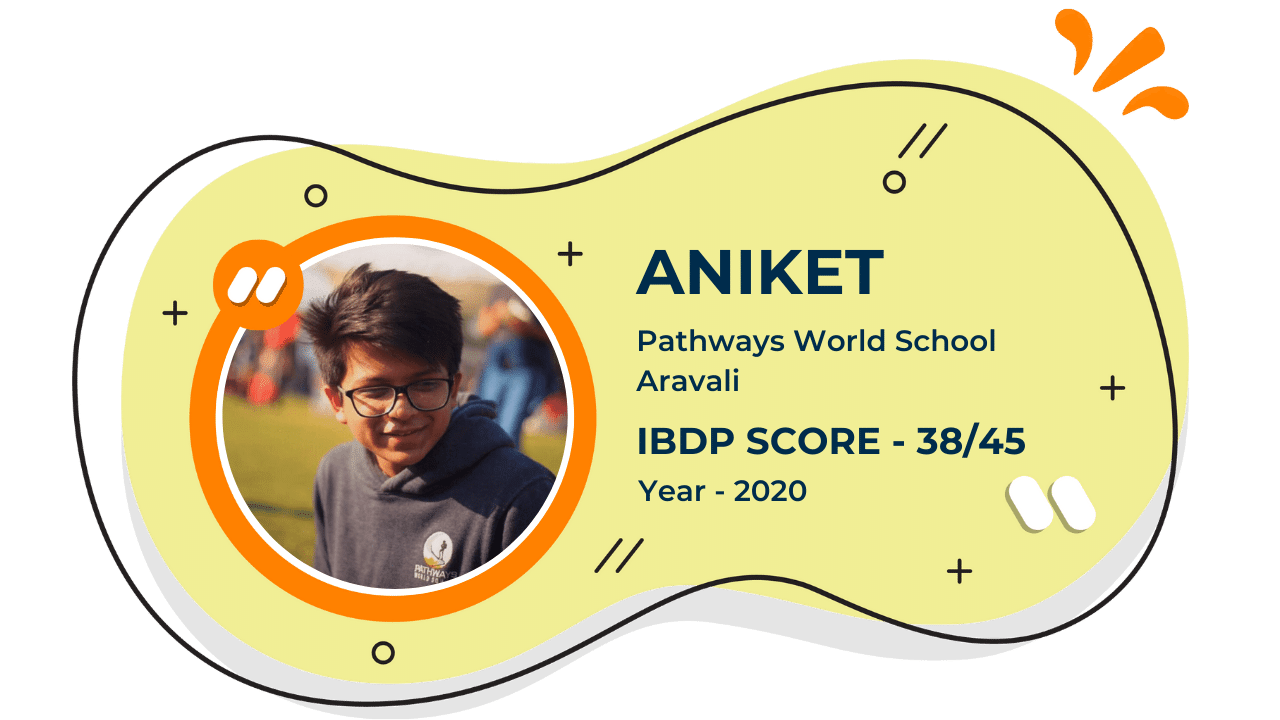
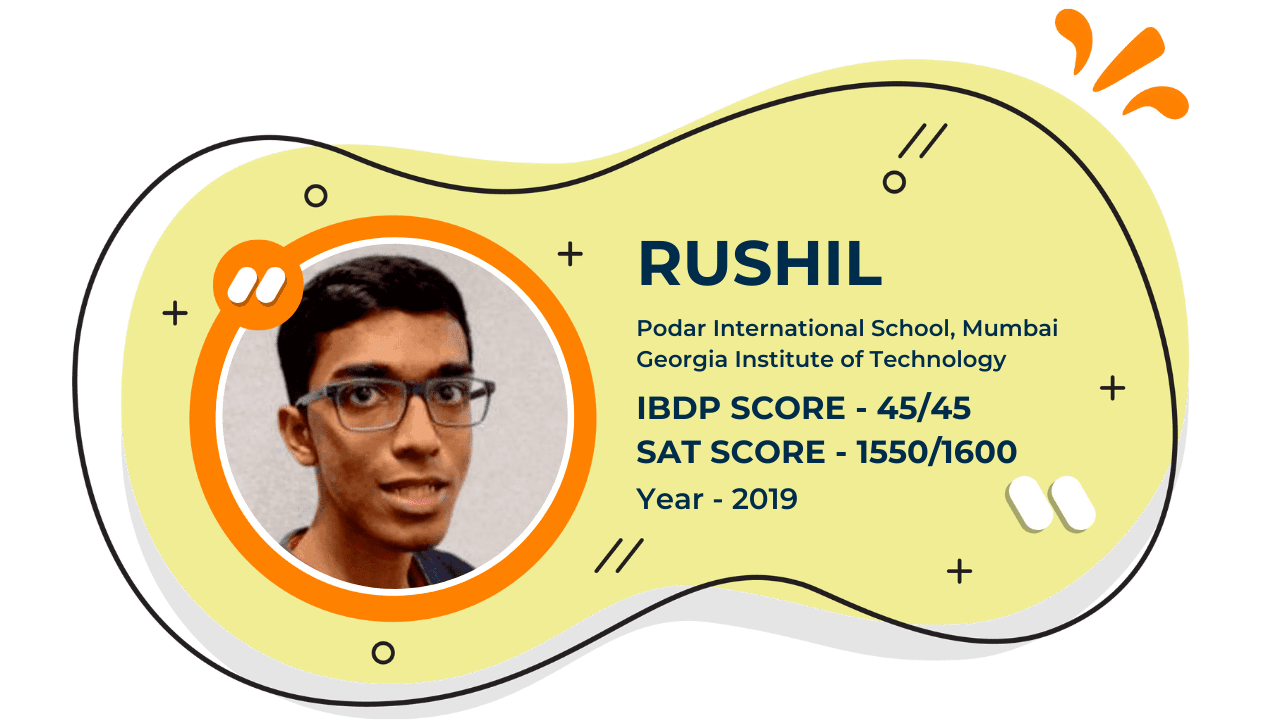
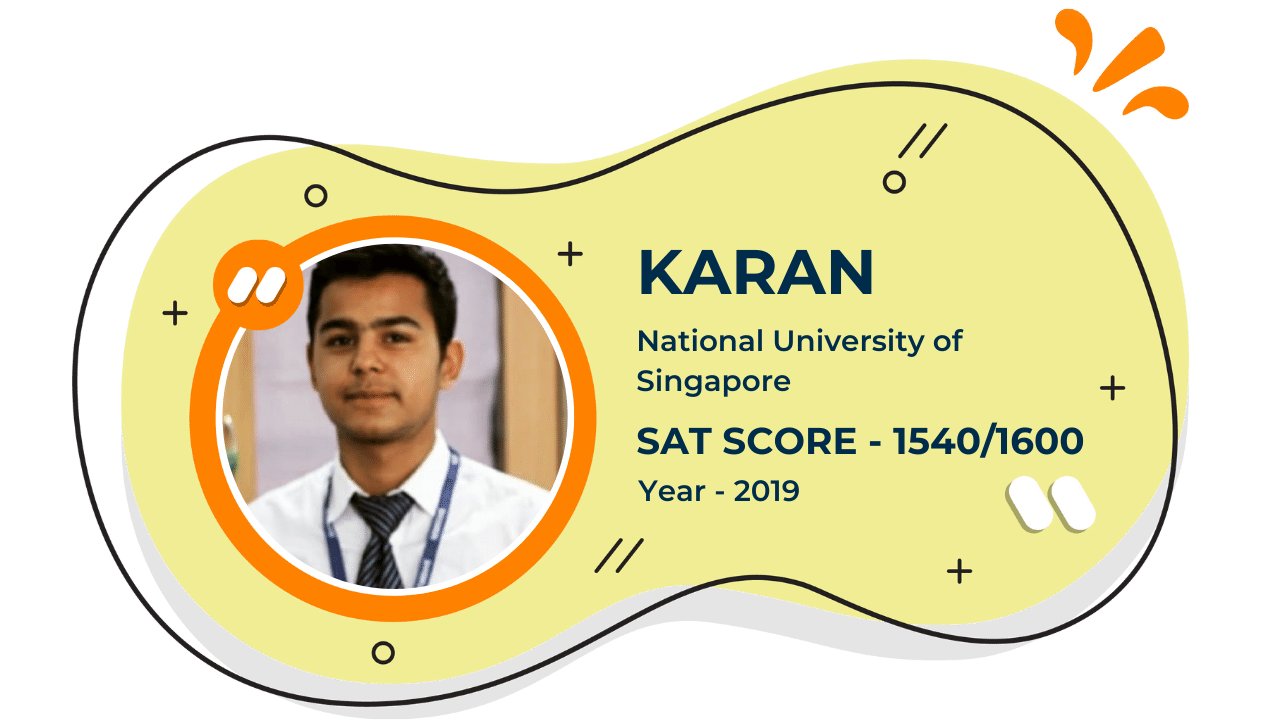
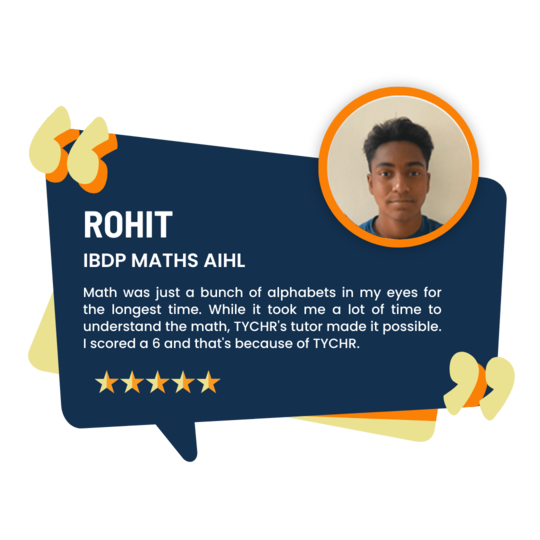
What our Students Have to say
A few words about us from our students…








FAQs – IB Maths Application & Interpretation TUITION Classes
A few frequently asked questions
Depending on their policies, several institutions recognise and grant credit for IB Maths AI. It’s best to verify with specific colleges about their credit transfer procedures.
IB Maths AI graduates can pursue jobs as data analysts, financial analysts, economists, business intelligence analysts, market research analysts, actuaries, operations research analysts, urban planners, and social scientists. This program’s applied mathematics abilities are useful in a variety of fields, including business, finance, research, and planning.
SYLLABUS COMPONENT | Recommended Teaching Hours | |
SL | HL | |
Syllabus content | 150 | 240 |
| 16 31 18 36 19 | 29 42 46 52 41 |
Development of investigational, problem-solving and modelling skills and the exploration of an area of mathematics | 30 | 30 |
IB Mathematics Applications and Interpretation (AI) covers key areas such number and algebra, functions, geometry and trigonometry, and statistics and probability. The course focuses on real-world applications, allows for optional topic investigation, contains an internal evaluation incorporating a practical mathematical inquiry, and finishes with external tests that measure theoretical and applied knowledge. This methodology attempts to provide students with adaptable mathematical abilities that are relevant in a variety of practical scenarios.
Type of Assessment | Format of assessment | Time(Hours) | Weighting of final grade% | ||
SL | HL | SL | HL | ||
External | |||||
Paper 1 | Technology allowed. Compulsory short-response questions based on the syllabus. | 1.5 | 2 | 40 | 30 |
Paper 2 | Technology allowed. Compulsory extended-response questions based on the syllabus. | 1.5 | 2 | 40 | 30 |
Paper 3 | Technology allowed. Two compulsory extended-response problem-solving questions. | 1 | 20 | ||
Internal | |||||
Exploration | 15 | 15 | 20 | 20 | |
IB Maths AI offers learners a practical and relevant grasp of mathematics, preparing them for university study in a variety of professions, particularly those that require quantitative abilities but do not place a large focus on theoretical mathematics.
IB MATHS AI Recent Blogs
Tychr’s Palette of Precision
How to Structure & Format Your Maths IA
Table of Contents1 Introduction:2 Structure of the Math IA:2.1 Introduction:2.2 Bad Introduction:2.3 Good Introduction:2.4 Mathematical Background:2.5 Exploration:2.6 Conclusion:2.7 Good Conclusion:2.8 References: Introduction: Mathematical exploration is an important part of the International Baccalaureate (IB) program, and writing a math Internal Assessment (IA) is a key requirement for students seeking to earn an IB diploma. The IA provides an opportunity for students to delve deeper into a mathematical concept of their choice, and to demonstrate their understanding and application of mathematical concepts and techniques. Math IA examples can serve as valuable references when embarking on your IA journey. Mathematics Analysis and Approaches (Math AA) is one of the two courses offered by the IB for Mathematics. Math AA focuses on developing students’ mathematical knowledge and skills in pure mathematics, including algebra, calculus, geometry, and trigonometry. Mathematics Applications and Interpretation (Math AI) is the other course that focuses on applying mathematics to real-world contexts, including statistics, probability, and modeling. Both Math AA and Math AI require students to complete an IA by the end of the course and the IA is an extremely important part of a student’s math grade. However, writing a successful math IA requires more than just a solid grasp of mathematical concepts; it also requires careful planning and structure. In this blog post, we’ll explore the key elements that make up a strong math IA structure, including the introduction, mathematical background, exploration, and conclusion. We’ll discuss the purpose and content of each section, and provide tips and strategies for crafting a clear and effective IA. Whether you’re just getting started on your math IA, or are looking to refine and improve your existing work, this blog post will provide valuable insights and guidance to help you succeed. Structure of the Math IA: The IA for both Math AA and AI follows a similar structure. Students are required to select a topic from one of the four areas of study: Algebra, Functions and Equations, Circular Functions and Trigonometry, and Calculus. The IA should be approximately 12-20 pages long, excluding appendices, and must contain the following components: Introduction: In this section, you should introduce the topic you have chosen and explain why it is important or interesting. You should also include a clear statement of the aim and objectives of your IA. A well-crafted introduction, like in the following maths IA examples, can engage your readers and set the stage for your exploration: Bad Introduction: In this math IA, I will explore the topic of calculus. Calculus is a branch of mathematics that deals with rates of change and slopes of curves. I will look at some calculus concepts such as derivatives and integrals and try to explain them in simple terms. This will help readers understand the basics of calculus. Why it’s bad: This introduction is too broad and does not provide a clear focus for the IA. It is also not engaging and doesn’t grab the reader’s attention. Good Introduction: Have you ever wondered how the trajectory of a soccer ball is calculated after it’s been kicked? What about the math behind predicting the weather or designing roller coasters? All of these scenarios involve the application of calculus, a branch of mathematics that allows us to understand the behavior of curves and rates of change. In this IA, I will explore the concepts of calculus through real-world examples, demonstrating how it can be used to solve complex problems and enhance our understanding of the world around us. Why it’s good: This introduction sets up the IA by engaging the reader with real-world scenarios and providing a clear focus on exploring calculus. It also hints at the importance and relevance of the topic, making the reader interested to learn more. Mathematical Background: This section should include a brief overview of the mathematical concepts and techniques that you will be using in your IA. It is important to show a deep understanding of mathematical theory and to provide clear explanations of any equations or formulas you will be using. You can find that in most Math IA examples or sample IAs often begin with a solid mathematical foundation: Bad Mathematical Background: The background is too general and does not provide specific information on the mathematical concepts that will be used in the IA. It does not indicate the level of mathematical knowledge that is required to understand the IA. It does not provide any context or motivation for why these mathematical concepts are important. Good Mathematical Background: The background provides specific information on the mathematical concepts that will be used in the IA. It indicates the level of mathematical knowledge that is required to understand the IA. It provides context and motivation for why these mathematical concepts are important. It is written in clear and concise language that is easy to understand. It may include references or additional resources that readers can use to refresh their knowledge of the relevant mathematical concepts. Exploration: This is the most substantial section of your IA and should demonstrate your ability to use mathematical tools to solve a real-world problem. You should explain the methodology used to investigate the problem and provide clear evidence of your calculations and reasoning. It is important to show your work clearly, including any graphs or diagrams you create look at some of these math ia exploration examples Bad Exploration Section: The exploration is too simplistic and does not demonstrate a deep understanding of the mathematical concepts being discussed. The methodology used to explore the mathematical concepts is not clearly described, making it difficult for readers to follow the logic of the argument. There is no data or evidence provided to support the conclusions drawn in the exploration. The exploration does not connect the mathematical concepts to any real-world applications or examples. Good Exploration Section: The exploration demonstrates a deep understanding of the mathematical concepts being discussed, and provides a clear explanation of how these concepts are being applied. The methodology used to explore the mathematical concepts is clearly
7 Tips to get a 7 in IB Maths AA HL
Table of Contents1 Check what course your college wants2 Math AA is more focused on the theory of mathematics3 The IB MATH IA is even more important than you think!4 Don’t be overly dependent on your calculator5 Ask questions in class6 Use online resources to improve your understanding7 Practice with Past Exams8 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)8.1 Q1: What is IB Maths AA HL?8.2 Q2: Is it difficult to get a 7 in IB Maths AA HL?8.3 Q3: What are some tips for getting a 7 in IB Maths AA HL?8.4 Q4: What resources are available for IB Maths AA HL students?8.5 Q5: What are the benefits of getting a 7 in IB Maths AA HL? The IB Math courses might seem confusing at first since they are not organized by topic (Geometry, Precalculus, etc.), but rather into two 2-year courses: Applications and Interpretation and Analysis and Approaches. So, what is the difference between them, and which one should you take? Here, we take a look at Maths AA HL, and discuss 7 ways to get a 7 in this course: Check what course your college wants Many colleges require you to take a particular IB Math course or require you to take HL instead of SL. Even if you are not certain which colleges you are applying to, think about what courses and colleges you might want to apply to—you don’t want to limit your options later by choosing the wrong course now. Also check if your colleges offer course credit for any of the IB courses, which would allow you to skip an introductory college course later. Math AA is more focused on the theory of mathematics This makes it suitable for those who want a rigorous, theoretical understanding of mathematics, particularly calculus. If you are planning to pursue a career in science, mathematics, or engineering, this could be important. The IB MATH IA is even more important than you think! Since there is a syllabus change, there is still a good bit of uncertainty about how the examinations will turn out. So, it is a good idea to maximize your score on the internal assessments by putting in a bit of extra effort there. Don’t be overly dependent on your calculator For IB Math AA, you need to take one test without a calculator. You should be confident in performing basic calculations, including simple trigonometric and algebraic operations, without a calculator. This might require a lot of practice, so make sure to use manual calculations from the beginning which could eventually boost your speed in a way that you won’t have to worry about the time required to solve during exams. Ask questions in class It’s important to iron out any misconceptions at the earliest. Don’t be afraid to ask your teacher to go over something you didn’t understand once more. You really do need to have a very solid conceptual understanding for this course.Only by setting the right foundation will you be confident to face any questions. Use online resources to improve your understanding If you think you’re still struggling to really understand something, try looking for resources and explanations online for IB Math. There are a lot of videos and articles that are not specific to this course but nonetheless will give you a good intuition for the material you are covering. Practice with Past Exams Even though this is a new syllabus, many of the actual exam questions will be on topics covered in the old Math HL course, and the pattern of questions might also be similar. Practicing with past exams is the best way to improve your problem-solving and time management skills. This would be especially helpful for people who get extremely anxious and blank out while the tests are given. Math is fun once you understand how it works, so don’t hesitate to ask for help, it may not be because you are less intelligent but probably you missed your basic foundation on the topic. You could either approach your own teachers, friends or rely on good tuition to build on lost foundations. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Q1: What is IB Maths AA HL? A: IB Maths AA HL is one of the math courses offered in the International Baccalaureate (IB) program. It is a higher-level course that covers topics in calculus, algebra, geometry, and statistics. Q2: Is it difficult to get a 7 in IB Maths AA HL? A: Yes, getting a 7 in IB Maths AA HL is considered challenging since it requires a deep understanding of the concepts, good problem-solving skills, and consistent effort throughout the course. Q3: What are some tips for getting a 7 in IB Maths AA HL? A: Some tips for getting a 7 in IB Maths AA HL include practicing regularly, seeking help from teachers or tutors when needed, and reviewing past exam papers to understand the format and style of questions. It’s also important to stay organized and manage your time effectively. Q4: What resources are available for IB Maths AA HL students? A: There are several resources available for IB Math AA HL students, including textbooks, online videos and tutorials, practice problems and exams, and study groups or forums. Your school or teacher may also provide additional resources and support. Q5: What are the benefits of getting a 7 in IB Maths AA HL? A: Getting a 7 in IB Maths AA HL can open up many opportunities for further study in fields such as engineering, science, finance, and economics. It also demonstrates a high level of proficiency in math and can boost your overall IB score and university application.
Get access to our free IB resources
Weave the Words of Success at TYCHR!

IB Math AI HL Paper 1 Question Bank

IBDP Mathematics AI HL Study Notes

IB Mathematics AI IA Ideas